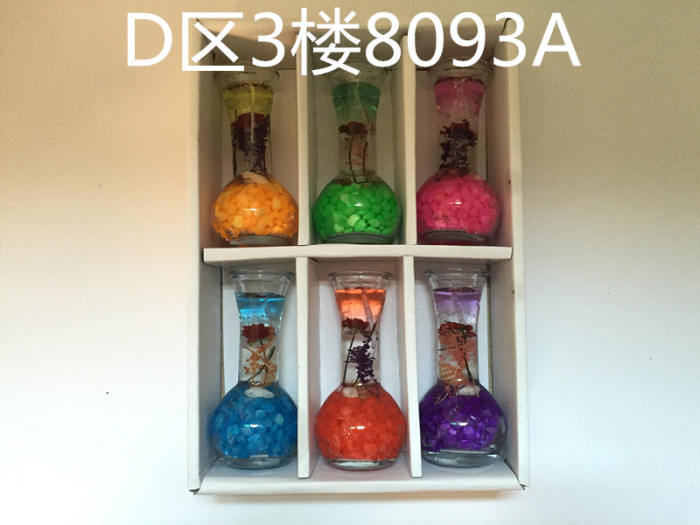
The main performance indicators of paraffin are melting point, oil content, and stability.
melting point
Paraffin is a mixture of hydrocarbon, so it does not have a strict melting point like pure compounds. The so-called melting point of paraffin refers to the temperature at which the mixture begins to melt.
refers to the temperature at which the cooling curve of a melted paraffin specimen first shows a period of stagnation under specified conditions.
All kinds of wax products require good temperature resistance of paraffin, which means they do not melt or soften and deform at a specific temperature.
According to the differences in usage conditions, the regions and seasons where the product is used, and the differences in the environment, the wax must have a series of different melting points.
The main factors affecting the melting point of paraffin are the weight of the raw material fraction used, and the melting point of paraffin obtained from heavier fractions is higher.
In addition, the oil content has a significant impact on the melting point of paraffin. The more oil in the paraffin, the lower its melting point will be.
Oil content
The oil content refers to the amount of low-melting point hydrocarbons in paraffin. High oil content can affect the color and storage stability of paraffin, and also reduce its hardness.
Therefore, the oil-containing wax paste obtained from the decompression fraction must be de-oiled using the sweating method or solvent method to reduce its oil content.
However, most wax products require a small amount of oil, which is beneficial for improving the luster and demolding performance of the products.
Stability
Paraffin products, which are in a hot-melt state for a long time during molding or coating and come into contact with air, are prone to oxidation and deterioration if their stability is poor, leading to darkening of color and even emitting a foul odor.
In addition, paraffin wax may turn yellow when exposed to light. Therefore, it is required that paraffin wax has good thermal stability, oxidation stability, and light stability.
The main factors affecting the stability of paraffin are the trace amounts of non-hydrocarbon compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons it contains. In order to improve the stability of paraffin, it is necessary to conduct deep refining to remove these impurities.