
Search history
Clear allSearch by image
XDrag and drop an image here or upload an image
Max 5MB per image
UploadSign In | Join

Search history
Clear allSearch by image
XDrag and drop an image here or upload an image
Max 5MB per image
UploadSign In | Join
X Email Mobile
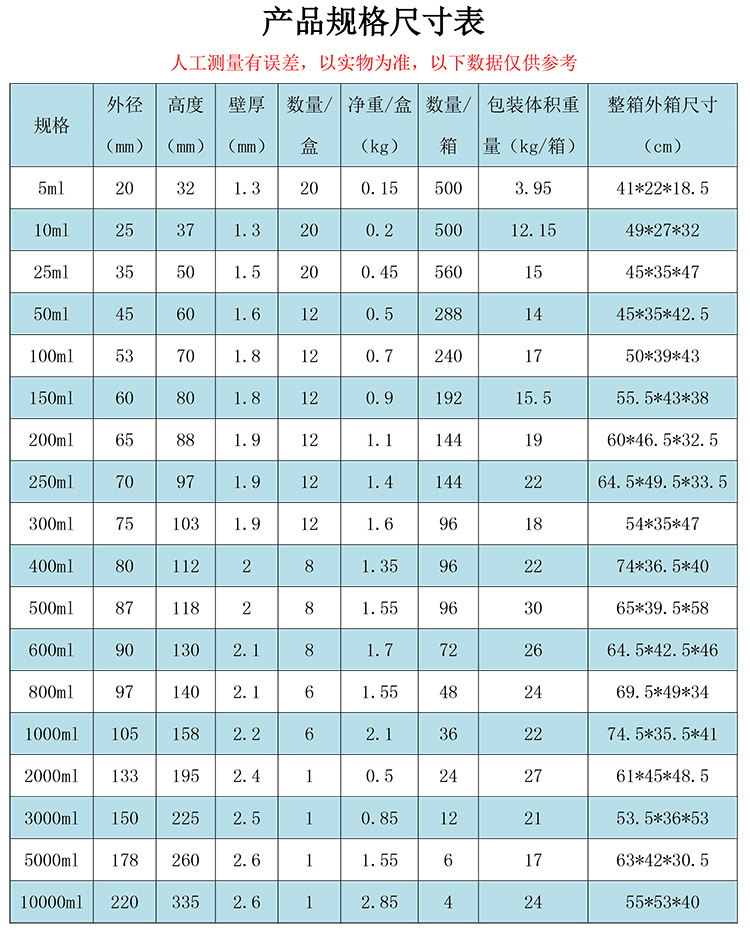
| 5ml | CN¥ 0.9 |
| 10ml | CN¥ 0.95 |
| 25ml | CN¥ 1.0 |
| 50ml | CN¥ 1.2 |
| 100ml | CN¥ 1.3 |
| 150ml | CN¥ 1.7 |
| 200ml | CN¥ 2.0 |
| 250ml | CN¥ 2.1 |
| 300ml | CN¥ 2.7 |
| 400ml | CN¥ 2.6 |
| 500ml | CN¥ 3.2 |
| 600ml | CN¥ 4.4 |
| 800ml | CN¥ 6.5 |
| 1000ml | CN¥ 7.0 |
| 2000ml | CN¥ 18.0 |
| 3000ml | CN¥ 30.0 |
| 5000ml | CN¥ 55.0 |
| 10000ml | CN¥ 170.0 |
| stick label | CN¥ 0.1 |
| glass stick 15cm | CN¥ 0.4 |
| glass stick 20cm | CN¥ 0.45 |
| glass stick 30cm | CN¥ 0.6 |
| glass stick 40cm | CN¥ 0.8 |
| high beaker 250ml | CN¥ 2.5 |
Yiwu Conor medical equipment Co., LTD 2yr.
Contacts:Amina Chat
Mobile:86-15058651598
E-mail:785069582@qq.com
Please click to purchase glass sticks.
Our company is a physical entity combined with online sales, specializing in the production and sales of physical, chemical, and biological experimental instruments for primary, junior, and senior high schools. We are a member unit of the China Teaching Industry Association.



Update time:
TOP